|
|
|
|
Diffusion
weighted analysis
The diffusion weighted imaging (DWI)
analysis referrs to analysis of diffusion weighted MR images aquired using 1
or 3 diffusion encoding gradient directions. Prior to initiating this
analysis module, it is of vital importance that the images are recognized as
a 4-dimensional time-series (for multi-slice DWI images), and that the images
are sorted according to image-number. This will be the case by default if the
images were loaded either using the DICOM reader interface (see “ DICOM Reader ” ) or
the DICOM server interface (see “ DICOM database ” ). Once loaded, the Diffusion
Weighted Imaging tab can be displayed by selecting Diffusion
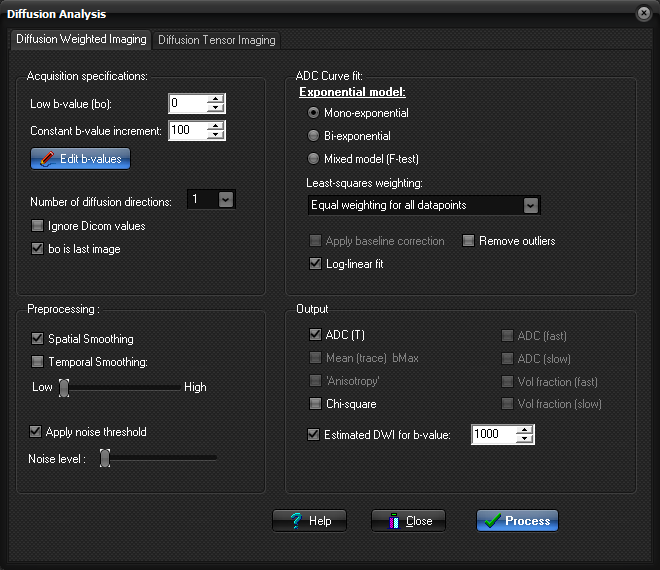
Analysis (DWI) on the Modules menu. Diffusion analysis settings.
nordicICE
should be able to determine the acquisition specifications of the loaded
dataset in most cases. If this fails, you need to know both the number of
diffusion directions and corresponding b-values inherent in the dataset. Acquisition specification:
Low b-value (b0): Specify the baseline (lowest) b-value. This is
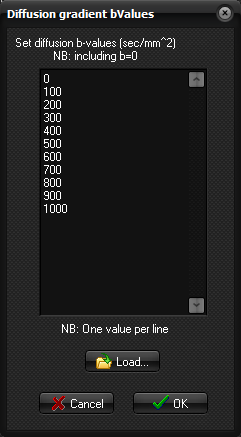
typically b0 but need not be so. Edit b-values: Used to specify the b-values of the diffusion
gradients. Any number of b-values can be analyzed and if more than two
b-values are used then a full non-linear exponential analysis is performed.
The b-values should be entered in units of sec/mm^2.
Example showing the setting of the b-values
for analysis of DWI data holding multiple b-values. The b-values should be
entered in units of sec/mm^2 and should include the b=0 value (if present in
the input images). NOTE: When performing the analysis, you may
get a message informing that there are too few b-values in the list, and that
some images are ignored. This can typically be the case if there are
additional images to the DWI images in the loaded series, such
as pre-calculated ADC-maps inserted by the scanner. These images will
then be excluded from the analysis. bo is last image : Check this box if the bo image appear as the last
images in the dataset. Default is that bo images appear as the first images. Preprocessing :
Spatial smoothing: Smooth the input image by applying the nearest-neighbor
averaging of each pixel value prior to processing. ADC Curve fit :
Exponential model: select between Mono-exponential (min. 2 b-values),
Bi-exponential (min. 3 b-values), or Mixed model (F-test).
F-value
(F-test): Specify p-value
threshold for F-test model fitting. Only used when Mixed model (F-test) is
chosen. Output :
For
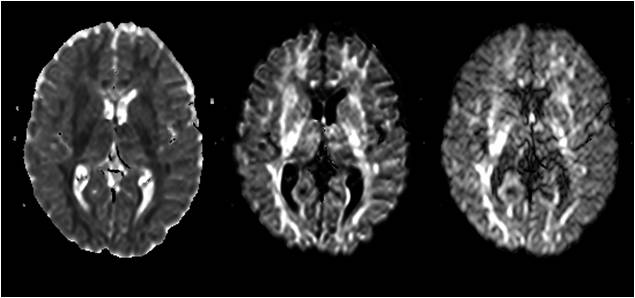
mono-exponential model: o ADC (T): Apparent Diffusion
Coefficient (Trace) image. The generated ADC (T) map is scaled so that the
pixels are in units of 10-5 mm2/s. For number of diffusion directions = 1,
the ADC map represents the ADC along the applied gradient direction. For 3
diffusion directions, the ADC(T) map is generated from the geometric mean of
the ADC in each of the three gradient directions. Applicable only to
mono-exponential model. o T2-corrected bMax: This map is similar to
the bMax images (where bMax represents the maximum b-value), but with the
T2-effect (also called 'T2-shine through') removed from the image. This is
done by calculating the theoretical signal intensity of the bMax image
according to the estimated ADC value. o bMax: This is simply a copy of
the bMax images from the input dataset and are only included for convenience
(e.g. for direct comparison with T2-corrected bmax images). Applicable only
to mono-exponential model. o 'Anisotropy': Generates a pseudo
anisotropy map based on the difference in ADC values in the three gradient
directions (based on the standard deviation of the trace map). This option is
only enabled for 3 diffusion gradient directions. Note that this image does
not represent true anisotropy since at least six gradient directions are
needed to determine anisotropy in three dimensions. o Estimate DWI image for b-value…: estimates the DWI image for a given b-value. This is done by
solving for fothe exponential expression for the scaling constant (A) with
the estimated ADC and user-supplied b-value. For bi-exponential and mixed model: o ADC (fast): Parametric map of
D_{fast} in the bi-exponential model. o ADC (slow): Parametric map of
D_{slow} in the bi-exponential model. o Vol fraction (fast): Parametric map
representing the volume fraction of the fast component, f_{fast}, in the
bi-exponential model. o Vol fraction (slow): Parametric map
representing the volume fraction of the slow component of, f_{slow}, in
the bi-exponential model. When applying the mixed model option
then only the D_fast map will contain non-zero values when a mono-exponential
fit is found optimal for a given pixel. Chi-square: Pearson’s cumulative test statistic for the
chi-square test on the sum of squared errors from the least-squares fitting.
Related topics:
DTI
(6 or more diffusion directions)
|